
Professional Coyote Removal in Milwaukee, WI
If you’re noticing a coyote repeatedly on your property, it may be time to contact the animal control professionals at Advanced Wildlife and Pest Control. Coyotes can pose a serious risk to small pets and, in some situations, children. Our certified wildlife removal specialists have the experience and training to safely trap, remove, and implement exclusion measures to prevent coyotes from returning to your home or business. Trust our wildlife experts to protect your home and family from the dangers coyotes pose.
Keep Raccoons Out of Your Yard!
Keep coyotes away with professional animal exclusion services in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Give Us a Call Today!Are Coyotes Dangerous?
Coyotes are wild animals that can pose a threat to both people and pets. Although they are typically shy and avoid human interaction, coyotes may become aggressive under certain conditions. Extra caution should be taken with children and pets, especially at night, when coyotes are most active. In addition to physical attacks, coyotes can carry diseases such as rabies, canine distemper, and mange, which may be transmitted to dogs and cats through bites or close contact.
- Coyote Identification -
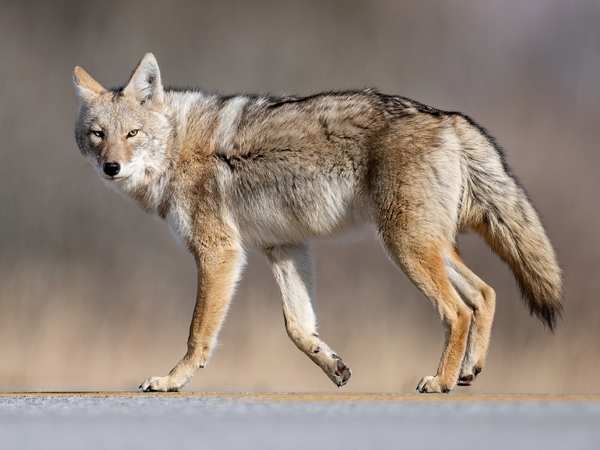
What Does a Coyote Look Like?
Coyotes are wild canines with narrow snouts and bushy, black-tipped tails. One way to tell coyotes from dogs is to watch their tails as they run. Coyotes hold their tails down between their hind legs, whereas dogs hold their tails up when running. Coyotes have coarse fur that is usually gray-brown, with subtle shades of red or yellow along the ears, face, and legs. Adult coyotes generally weigh between 20 and 40 pounds, stand about 2 feet tall at the shoulder, and measure approximately 3 to 4.5 feet in length, including the tail.

Behavior & Habits
Coyotes are primarily active from dusk until dawn and communicate using a wide range of vocalizations, including barks, yips, whines, and howls. They are social animals that may live in family groups or as solitary individuals, typically hunting alone or in pairs. Highly adaptable, coyotes thrive in a variety of environments and are increasingly common in suburban and urban areas, including Milwaukee. Coyotes do not hibernate during the winter; instead, they shed their lighter summer coats and grow thicker, heavier fur in the fall to help them withstand cold winter conditions.
Coyote Exclusion
Coyotes may enter residential properties in search of food, water, and shelter. While they generally avoid direct contact with people, coyotes have adapted well to living in residential areas throughout Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Our heavy-duty mesh fencing solutions are designed to keep coyotes from accessing areas beneath decks, porches, and sheds. The fencing is professionally installed and buried 12 to 18 inches deep to prevent burrowing and future intrusion. Contact our wildlife specialists today for effective coyote removal and long-term exclusion solutions.
- Coyote FAQs -
Frequently Asked Questions
What do coyotes eat?
Coyotes are carnivores that mainly prey on squirrels, rabbits, rodents, and other small mammals. Coyotes hunt in packs when hunting larger prey like deer. They prefer to eat fresh kill, but coyotes will occasionally eat carrion. In urban environments, coyotes may enter yards to feed on pet food or garbage. Coyotes may attack domestic pets if they come close to them on your property.
Where do coyotes live?
Coyotes are found throughout Wisconsin. They prefer open grasslands and woodlands. However, coyotes are very adaptable, and it is not uncommon to see coyotes living in suburban or urban areas in Milwaukee. Coyotes make dens out of existing burrows or covered areas. Underneath porches, decks, and sheds are potential places for coyotes to build dens.
When do coyotes have babies?
Coyotes mate between February and April. The gestation period is approximately two months, with pups born during late April or early June. Coyotes have one litter per year. Litters of two to nineteen pups have been recorded, but the average litter size is usually around five to seven. The pups are weaned when they are about a month old. Male pups will leave their mother when they are six and nine months old. Female pups will stay with their mother’s pack. Male and female coyotes pair off and mate together for several years.
How long do coyotes live?
The average lifespan of a coyote in the wild is about 10 to 14 years. Coyotes have a few predators, including wolves and bears. Unfortunately, many coyotes die due to human interaction: road kills, trapping, shooting, and farming chemicals.
What does coyote poop look like?
Coyote poop looks very similar to dog poop, but they often contain visible traces of small bones, fur, or plant matter. Coyote scat is usually found in the middle of trails or near the borders of their territories.
What do coyote tracks look like?
Coyote tracks are often confused with dog paw prints, but there are some distinguishing features. Coyote prints are more oval-shaped than dog prints, with two nail prints at the top of the paw and a larger heel impression. Coyote tracks will also appear in a straight line, whereas dogs frequently change direction, leaving a random track pattern. A coyote’s hind foot may also overlap the track of its front foot.
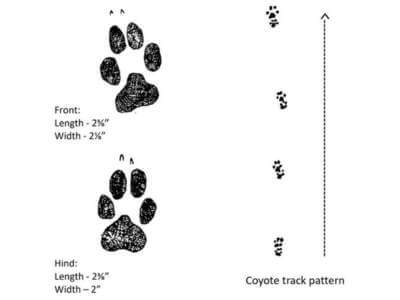
Illustration by Dan Goodman

