
Professional Beaver Removal in Milwaukee, Wisconsin
If you spot a beaver dam on your property, it is important to take immediate action. Beavers can cause significant damage to property, including cutting down valuable trees, damaging crop fields, and causing flooding. Advanced Wildlife and Pest Control specializes in beaver removal in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Our certified wildlife specialists have the expertise and equipment to safely trap and remove nuisance beavers, protecting your property while adhering to state wildlife regulations.
Keep Beavers Out of Your Property!
Get rid of beavers with our professional wildlife removal services in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Give Us a Call Today!Behavior & Habits
Beavers are often called “nature’s engineers” because of their innate ability to modify and reshape their environment. While their dams can sometimes cause issues for humans, this behavior plays an essential role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. By controlling water levels, beavers help form wetlands and other habitats that support fish, birds, and a variety of other wildlife. Primarily aquatic, beavers only venture onto land to forage for food. Since they do not hibernate, they must store supplies to survive the winter months. Although they typically cut smaller trees, beavers are capable of cutting down trees over five feet in diameter.
- Beaver Identification -
What Does a Beaver Look Like?
Beavers are the largest rodents in Wisconsin, with adults reaching 3 to 4 feet in length and weighing between 25 and 60 pounds. They have reddish-brown fur and a large, flat tail covered with dark, leathery scales. Adapted for life in the water, beavers have webbed hind feet and a broad tail that aid in swimming and maneuvering. Beavers have small eyes and ears, and their nose has valves that close when they are underwater. They are excellent swimmers and can hold their breath for up to 15 minutes. Beavers also have large orange-red incisors that allow them to chew through wood.

Beaver Damage
Beavers use their sharp incisors to cut down trees to form lodges and dens. In urban areas, beavers may damage valuable trees and shrubs. Beavers can cause flooding by building dams that block drainage ditches, streams, and culverts. While the habitats beavers create may offer short-term benefits for other nearby wildlife, they can have long-term negative impacts on streams and ecosystems.
Beaver Diseases
Beavers can transmit diseases like tularemia and giardiasis (beaver fever) to humans. These illnesses are typically transmitted through direct contact with infected animals, drinking contaminated water, and tick bites. Do not drink water where beavers are present. Symptoms of tularemia include skin ulcers, swollen lymph glands, inflamed eyes, diarrhea, and sore throat. Symptoms of giardiasis include watery stools, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and dehydration.
- Beaver FAQs -
Frequently Asked Questions
What do beavers eat?
Beavers are herbivores. Most of their diet consists of tree bark and cambium, the soft tissue that grows under the bark of a tree. Beavers especially like the bark of willow, maple, birch, aspen, cottonwood, beech, poplar, and alder trees. They will also eat aquatic plants such as water lilies, duckweed, and cattails.
Where do beavers live?
Beavers are herbivores. Most of their diet consists of tree bark and cambium, the soft tissue that grows under the bark of a tree. Beavers especially like the bark of willow, maple, birch, aspen, cottonwood, beech, poplar, and alder trees. They will also eat aquatic plants such as water lilies, duckweed, and cattails.
When do beavers have babies?
Beavers are monogamous, which means they mate with one partner for life. The mating season for beavers in Wisconsin usually takes place from January to February. After a gestation period of about three months, female beavers give birth to two to four kits between late April and July. The young beavers are weaned at around two months of age and stay with their parents for two years. An established colony of beavers consists of an adult pair and two years of offspring.
How long do beavers live?
The average lifespan of a beaver in the wild is ten to twelve years. Coyotes, foxes, bobcats, bears, and wolves prey upon beavers.
What does beaver poop look like?
Beaver scat consists mainly of wood chips. The oval pellets are 1 to 2 inches long and look like a mix of sawdust, woodchips, and mud in a snowball shape. Beaver droppings are hard to find since they defecate in the water and disintegrate quickly.
What do badger tracks look like?
Badgers walk in a pigeon-toed fashion, so their tracks point inward. They have large paws, which leave wide and blocky imprints. The front tracks measure 2-3 inches long and 2 inches wide. The front claws are very long and extend about an inch ahead of their toes, leaving noticeable marks. The hind tracks are slightly smaller, and the rear claw marks usually do not make an imprint.
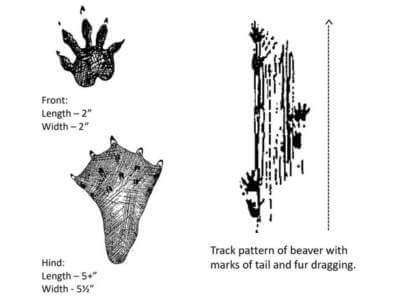
Illustration by Dan Goodman
