What Does a Deer Look Like?
Deer is an all-encompassing term used to represent a wide variety of hoofed animals, such as white-tailed deer, elk, and moose. In Wisconsin, the most common species of deer is the white-tailed deer. White-tailed deer stand 3 to 3 1/2 feet tall. Adult males (bucks) weigh 150 to 250 pounds, and adult females (does) weigh 100 to 150 pounds. During the summer, the fur of both sexes is reddish-brown to tan, and in the winter, it is grayish-brown. The upper throat, belly, inner rump, and underside of the tail are white. Young deer (fawns) have a reddish coat with white spots that act as camouflage to help them blend into the ground. Only male deer grow antlers, which are grown and shed each year.
Deer Damage
Deer can cause significant damage to orchards, nurseries, landscaping, farms, and home gardens with their feeding. Male deer also use tree trunks to trim their antlers, which can lead to bark damage and even the death of trees. Additionally, white-tailed deer carry deer ticks, which can spread Lyme disease to humans.

Deer Management in Milwaukee, WI
Wisconsin has a large population of white-tailed deer, with an estimated population of 1.6 million in 2020. According to the Wisconsin DNR, deer-vehicle collisions are a major safety concern for Wisconsin drivers. Between 15,000 and 19,000 deer are killed annually by vehicles on Wisconsin roadways. Regulated hunting is the primary method of deer control, but most suburban areas do not allow hunting.

Deer Deterrents & Repellents
Habitat modification and the use of repellents are considered the most effective ways to keep deer away from your gardens and landscaping. Fencing around gardens and flower beds can also serve as a deterrent to keep deer from eating your plants. Setting up posts around trees can provide male deer with another suitable structure to rub their antlers on, thus helping to protect the bark of the trees. At Advanced Wildlife and Pest Control, we utilize natural deer repellents to keep deer away from your plants and gardens. Contact us today for effective deer management solutions to protect your gardens and plants from deer.
Dead Deer Removal Service
If an injured deer wanders onto your property and dies, our wildlife removal professionals can remove the dead deer from your property. There is a fee for our dead deer removal service. Contact us today for immediate help!
Deer FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
What do deer eat?
The white-tailed deer is an herbivore or plant eater. A deer’s diet changes depending on its habitat and the season. It eats green plants in the spring and summer. In the fall, it eats corn, acorns, and other nuts. In the winter, it eats the buds and twigs of woody plants. In an urban environment, deer may damage plants in vegetable gardens or landscaping.
Where do deer live?
White-tailed deer thrive in various habitats, including forests, farmlands, open fields, and wooded areas. Deer prefer thinly wooded areas near streams and open agricultural areas with easy access to food and protection from predators. Deer are also found in very developed urban areas of Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
When do deer have babies?
White-tailed deer mate from October through January, with the peak occurring in mid-November. Gestation is about 6 to 7 months, with most fawns born in late spring. Fawns can walk and run within a few hours of birth. They are weaned at about six weeks. The fawns are reddish-brown at birth, with white spots that help camouflage them. The mother leaves her fawns well-hidden for hours at a time while she feeds. While waiting for their mother to return, the fawns lay on the ground with their heads and necks stretched out flat, making it harder for predators to find them. Female fawns stay with their mother for two years. Males usually leave after a year.
How long do deer live?
The average lifespan of a white-tailed deer in the wild is about 4 to 6 years. White-tailed deer have several predators, including coyotes, wolves, bears, and bobcats. Unfortunately, many deer die as a result of human interaction, such as road kills and shooting.
What does deer poop look like?
White-tailed deer droppings are dark, cylindrical pellets 1/2 - 1 inch long. The droppings look similar to those of rabbits, but deer will produce much larger deposits of solid scat and clumped pellets.
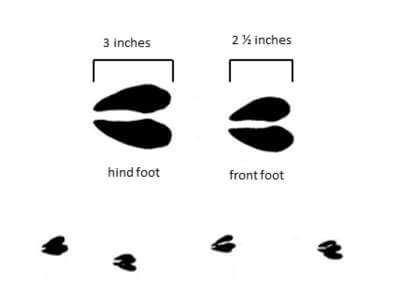
What do deer tracks look like?
The heart-shaped tracks of white-tailed deer are easy to identify. The deer has two hoofed toes that come to a point at the front. Adult deer tracks measure 1 to 4 inches long and 3/4 to 3 inches wide.