
Professional Raccoon Removal in Milwaukee, WI
Advanced Wildlife and Pest Control provides rabbit removal and exclusion services in Milwaukee and southeastern Wisconsin. Our certified wildlife specialists safely and efficiently trap, remove, and exclude nuisance rabbits from homes and businesses.
We begin with a thorough inspection to identify signs of rabbit activity, including droppings, tracks, burrows, and vegetation damage. Our team then sets live traps to humanely capture rabbits. Live trapping is the most effective and humane method for removing rabbits from your property.
Keep Rabbits Out of Your Yard!
Get rid of rabbits with our animal control and exclusion services in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Give Us a Call Today!What are the Signs of a Rabbit in Your Yard?
Cottontail rabbits thrive in areas with dense vegetation or agricultural landscapes that provide ample grass and plants for grazing and cover. They often take shelter in brush piles, wood piles, shrubs, and tall grass. When conditions allow, rabbits may burrow under porches, decks, or sheds. Typically, a single rabbit will remain within a 10-acre area for its entire life, rarely venturing beyond unless food or cover becomes scarce.
- Rabbit Identification -
What Does a Rabbit Look Like?
The eastern cottontail is the most common rabbit species in Wisconsin. It has a speckled brown-gray coat with reddish-brown fur around the neck and feet, and a white underside. Cottontails have long ears, large hind feet, and short, fluffy white tails that resemble cotton balls. Adults typically measure about one foot in length and weigh between 1 and 6 pounds.

Rabbit Damage & Diseases
Rabbits are voracious eaters, feeding throughout the day on flowers, vegetables, herbs, and grasses. If left unchecked, they can cause significant damage to gardens, flower beds, landscaping, and crop fields. In addition, wild rabbits may carry tularemia, also known as “rabbit fever,” a bacterial disease that can be transmitted to humans through tick or flea bites.
Rabbit Prevention
The most effective way to prevent rabbits is through exclusions and habitat modifications around your home. Our heavy-duty wire mesh fencing can keep rabbits from burrowing under decks, porches, and sheds. The fencing is buried 12 to 18 inches deep to block underground access. Installing fencing around gardens, orchards, and flower beds can also help protect plants from rabbit feeding.
- Remove brush piles, weed patches, stone piles, and other debris.
- Clean up fallen fruit and vegetation from your property.
- Put up a barrier around your flowers and garden to keep them out.
- Block access underneath decks, porches, and sheds with our heavy-duty wire mesh fencing.
- Rabbit FAQs -
Frequently Asked Questions
What do rabbits eat?
Rabbits are herbivores and eat many kinds of plants, including grasses, clovers, alfalfa, and dandelions. They will also eat garden plants such as lettuce, peas, asparagus, cabbage, tomatoes, beets, beans, and more. In the winter, rabbits eat woody parts of plants like twigs and bark.
Where do rabbits live?
Eastern cottontail rabbits are found throughout Wisconsin, especially in grasslands, meadows, farmlands, and wooded areas. Rabbit burrows are often found near tree stumps or in tall, thick grasses.
When do rabbits have babies?
The eastern cottontail rabbit is polygamous and will mate with several rabbits. They mate from February through September. The gestation period is only 28 to 30 days, with four to six young born per litter. Cottontails often have three to four litters per year. Baby rabbits are born blind and hairless. They are weaned after about three weeks and leave the nest after about seven weeks. Eastern cottontails can mate when they are three months old.
How long do rabbits live?
The average lifespan of an eastern cottontail rabbit in the wild is one year. Coyotes, bobcats, foxes, hawks, snakes, and owls prey upon wild rabbits.
What does rabbit poop look like?
Rabbit droppings are small, dark, spherical, and less than 1/2 inch in diameter. Cottontails are coprophagous, meaning that they eat their own droppings.
What do rabbit tracks look like?
Rabbit footprints are oval in shape, with five toes on the front feet and four toes on the hind feet. The prints of their hind feet are about double the length of the prints of the front feet. When rabbits hop, the prints of the hind feet are side by side in front of the prints from the front feet.
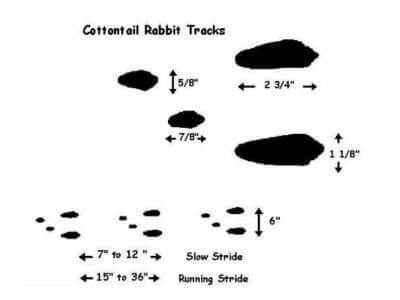
Illustration by Jenavieve Mueller

